[GSE2022]Forum on Promoting Digital Literacy in Smart Learning Environment
date:2022-09-29 14:36author:adminsource:Smart Learning Instituteviews:
With the smart technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data continuing to mature, these technologies have penetrated into all areas of human activity, changing the way they produce, live, and learn. The widespread deployment of smart technologies is considered a core competitive advantage of sustainable development. At the center of this ecosystem of smart technologies is the users, aiming to improve digital literacy and promote smart learning. As a result, all levels of educational institutions around the world are challenged by the incremental or disruptive digital transformation and intelligent upgrading.
At the same time, in the wake of the Covid-19, distance learning has become a new reality in school education around the world, and blended teaching has been widely adopted in K-12, higher education, vocational education and lifelong learning. To this end, it is necessary to analyze the application scenarios of sustainable smart education and conduct dialogues around differentiated education and personalized learning with intelligent technology, including the issues on digital literacy and skills, technology-empowered smart learning, teaching innovation and smart learning environments, which provided new ideas and directions for countries to further improve citizens' digital literacy and promote smart learning practices.

Mr WANG Yongli, deputy president and secretary-general of the China Education Association for International Exchange
Mr WANG Yongli, deputy president and secretary-general of the China Education Association for International Exchange, expressed his expectations for the interconnection of higher education between regions. He noted that under the framework of the China-Central and Eastern European Universities Federation, China Education Association for International Exchange would fully support the international exchanges and cooperation between Chinese higher education institutions and those in Central and Eastern Europe, aiming to promote the high-quality development of global higher education.

Professor Vladan Đokić, the rector of the University of Belgrade
Professor Vladan Đokić, the rector of the University of Belgrade, said that the University of Belgrade and Beijing Normal University have extensive cooperation foundations and close ties in the field of smart education. He expected the two sides would carry out more in-depth cooperation in the field of educational technology.
Academic Network for Education of CCHEIC

Professor YU Kai, vice dean of the faculty of education of Beijing Normal University
Professor YU Kai, vice dean of the faculty of education of Beijing Normal University, launched the "Academic Network for Education of CCHEIC", and introduced the concept and action plan of the community construction. Professor Danimir Mandić from the University of Belgrade and professor Demetrios Sampson from the University of Piraeus hoped to strengthen the exchanges between universities, research institutions in Central and Eastern European countries (CEEC) and Chinese universities in the field of education, which aimed to promote the sharing of high-quality educational resources, deepen the pragmatic cooperation between countries in the aspects of educational theory research and educational practice innovation, and finally contribute to building a community with a shared future for mankind.
The Academic Network for Education of China-CEEC Higher Education Institutions Consortium (CCHEIC)
China-CEEC Higher Education Institutions Consortium (hereinafter referred to as “Consortium”) was established in 2014. On the basis of adhering to the “mutual respect, equality and mutual benefit, and win-win cooperation” principle, the Consortium plays an important role in enhancing educational exchanges and cooperation between China and central and Eastern European countries. China Education Association for International Exchange (hereinafter referred to as
“Association”), as the Chinese Secretariat, continues to expand the influence of the Consortium, gives full play to the initiative and enthusiasm of its member universities, and plans to implement the classified management of the academic network. As the co-founder, Beijing Normal University applies to initiate the Academic Network for Education of China-CEEC Higher Education Institutions Consortium. Beijing Normal University is responsible for absorbing Chinese and foreign universities in the educational field; planning cooperative projects to jointly build and promote the development of educational disciplines; and manage the activities of member 2 universities in the academic network.
· Goal
Relying on the platform of Consortium, the academic network aims to strengthen academic exchanges and cooperation in the field of educational disciplines between China and CEE countries; to carry out cooperation in brand projects, and build a network for academic cooperation and exchanges among member universities; to promote the sharing of high-quality educational resources, and to support international joint research; raise the internationalization level of educational research
· Goal
Relying on the platform of Consortium, the academic network aims to strengthen academic exchanges and cooperation in the field of educational disciplines between China and CEE countries; to carry out cooperation in brand projects, and build a network for academic cooperation and exchanges among member universities; to promote the sharing of high-quality educational resources, and to support international joint research; raise the internationalization level of educational research
and practice; cultivate innovative talents with global competence, and make greater contribution to building a community with a shared future for mankind.
· Mission
· Mission
Under the guidance of the Bucharest Guidelines for Cooperation between China and Central and Eastern European Countries, the academic network focusing on the work of Opening-up of Education in the new era and following actual needs of educational discipline development in China and CEE countries. Abide by the principles of mutual learning, co-building and sharing, cooperation and development, through “building platforms, sharing resources, building brands, and joint output” series activities, the academic network will strengthen exchanges and cooperation in education disciplines between China and CEE countries, and jointly cultivate innovative talents with strong abilities to meet global challenges.3
· Obligations
The Association is responsible for managing and supervising of all community work, including to determine the sub-group plan of the Consortium and issue the working methods; monitor and review the work of the academic network; to provide necessary assistance as required by the academic network universities; and participate in the annual meeting, etc.
Beijing Normal University is responsible for coordination of the members and carrying out activities within the academic network, including organizing the management and working team; drafting the application methods; planning and designing cooperation projects and annual development plans; developing universities in China and CEE countries as Consortium member universities; organizing academic activities and monitoring the progress of cooperation projects; and working on the annual summary of academic network activities.
· Work Plan
Establish academic network team and build a cooperative network
Establish academic network team
Create cooperation and exchange brand projects
Sharing educational resources and cooperating to cultivate talents
Implementation of high-quality education resource sharing projects
Cooperative development of postgraduate courses
Organizing student exchange programs
Conducting campus cultural activities of mutual learning and appreciation to enhance the global competence of students
Strengthening joint scientific researches and joint publications in the Academic Network for Education
Carrying out workshops for principals and teachers of primary and secondary schools in China-CEE countries
Providing theoretical support and professional guidance for the China-CEE Education Community
· Obligations
The Association is responsible for managing and supervising of all community work, including to determine the sub-group plan of the Consortium and issue the working methods; monitor and review the work of the academic network; to provide necessary assistance as required by the academic network universities; and participate in the annual meeting, etc.
Beijing Normal University is responsible for coordination of the members and carrying out activities within the academic network, including organizing the management and working team; drafting the application methods; planning and designing cooperation projects and annual development plans; developing universities in China and CEE countries as Consortium member universities; organizing academic activities and monitoring the progress of cooperation projects; and working on the annual summary of academic network activities.
· Work Plan
Establish academic network team and build a cooperative network
Establish academic network team
Create cooperation and exchange brand projects
Sharing educational resources and cooperating to cultivate talents
Implementation of high-quality education resource sharing projects
Cooperative development of postgraduate courses
Organizing student exchange programs
Conducting campus cultural activities of mutual learning and appreciation to enhance the global competence of students
Strengthening joint scientific researches and joint publications in the Academic Network for Education
Carrying out workshops for principals and teachers of primary and secondary schools in China-CEE countries
Providing theoretical support and professional guidance for the China-CEE Education Community
Academic exchanges on smart education betwen China and (CEEC)
At this forum, 12 experts from 9 countries shared their understanding of the characteristics of smart education, as well as the latest situation and practice of smart education development in China and Central and Eastern European countries.

Ms ZHUANG Rongxia, associate professor of Beijing Normal University
Ms ZHUANG Rongxia, associate professor of Beijing Normal University, focused on international comparative research on the development of smarter education. Based on the cooperative research results from China, Serbia, Greece, and other countries, she analyzed the overall characteristics and characteristics of smart education practices in various countries and pointed out that smart education can be promoted from 3 aspects: the construction of smart learning environments, the reform of teaching and learning, and educational policy and governance. She held that smart education is a long-term, systematic, and continuous work that requires the joint efforts of all countries.
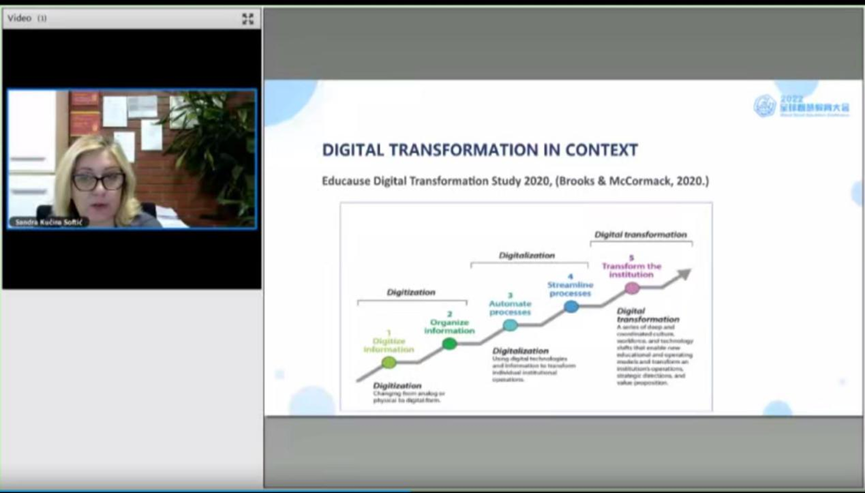
Professor Sandra Kucina Softic from the University of Zagreb
Professor Sandra Kucina Softic from the University of Zagreb elaborated on the advantages and challenges of digital transformation in Education. She believed the digitization of education has made teaching resources available to more learners on a global scale; as a result, students have a wider range of learning opportunities, and the learning process is more personalized. She also stressed that the digital transformation of colleges and universities needs to redevelop the operating model and integrate "digitalization" into education in an all-round way, rather than just adding high-quality digital infrastructure.

Mr Borut Čampelj, who is from the office of Development and Education of the Ministry of Education, Science and Sport in Slovenia
Mr Borut Čampelj, who is from the office of Development and Education of the Ministry of Education, Science and Sport in Slovenia, gave his view on the topic of ''Towards Smart Education". He believed smart education needs to consider the factors like smart curriculum, teaching environment, pedagogic methods, teachers, leadership team, etc. Smart education shall be developed with the aim to benefit various communities and promote ubiquitous, equitable and quality education.
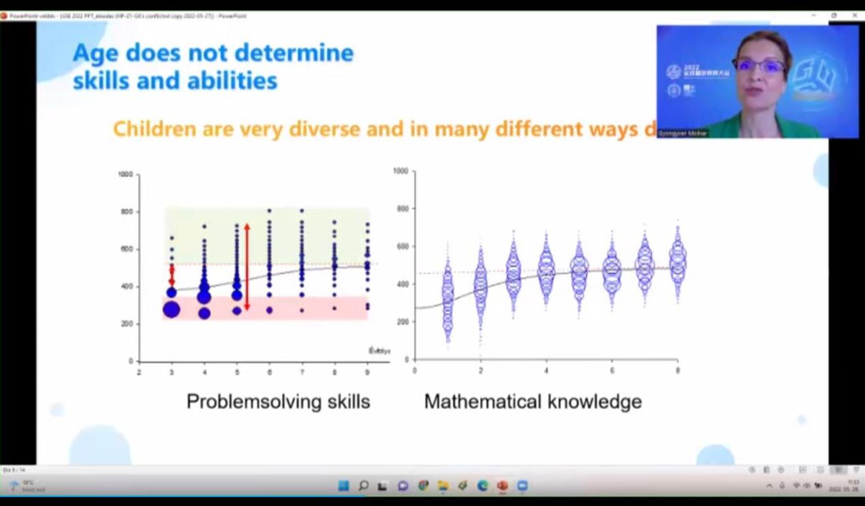
Professor Gyöngyvér Molnár from the University of Szeged in Hungary
Professor Gyöngyvér Molnár from the University of Szeged in Hungary gave a presentation on "Applying Intelligent Technology to Make Education Smarter". She proposed that intelligent education should be evidence-based, data-driven, and constantly adapt to students' individual needs. She emphasized that summative assessment cannot meet the individual needs of students, and it is necessary to develop complex, practice-integrated, high-quality assessment methods and tools to replace the traditional "one-size-fits-all" method.

Professor WANG Yunwu from Jiangsu Normal University
Professor WANG Yunwu from Jiangsu Normal University said that many countries around the world had implemented digital education strategies, which accelerated the digital transformation in education. The two-way empowerment of technology and education will further accelerate the digital transformation in education, form an ecological chain of digital education, and promote the development of the digital economy and smart society.
Dr. Diana Andone from the Politehnica University of Timisoara in Romania highlighted “Digital Future Universities 2030”. She introduced the framework for developing digital education strategies for universities. The framework includes 3 areas: “Vision, Leadership, Governance”, “People, Community, Stakeholders”, and “Tools, Spaces, Resources.” She also suggested that the collaboration and openness of all stakeholders shall be empowered, the sense of community needs to be created, and the infrastructure shall be scaled up.
In addition, 6 experts shared their views on the development of smart education in their own countries, including professor Siyka Chavdarova-Kostova from Sofia University "St. Kiment Ohridski" in Bulgaria, professor Charalampos Karagiannidis from the University of Thessaly in Greece, Dr. Engjellushe Zenelaj from the Reald University of Vlora in Albania, Dr. Maja Homen from the University of Zagreb in Croatia, and Ms Ana Sekulovska from the University of Tourism and Manegement Skopje in North Macedonia.


